RIC vs BTE Hearing Aids: Which Is Right For You?
If you have been advised by your audiologist that you require hearing


If you have been advised by your audiologist that you require hearing
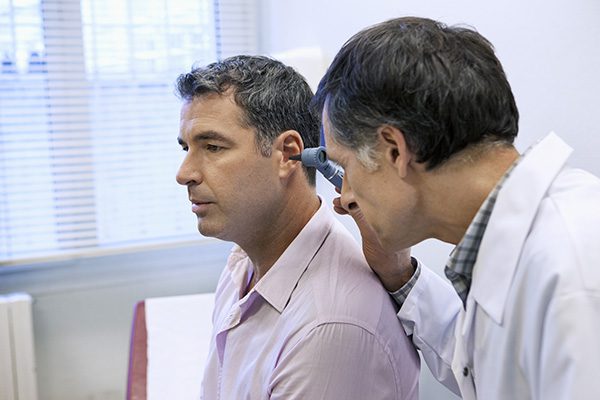
Have you started hearing unusual noises? Do they sound a bit like the
Your hearing is precious and doing everything that you can to protect it